Introduction
Welcome to my blog! In our rapidly changing tech world, businesses must build and maintain scalable apps to stay competitive. The 12-Factor methodology provides valuable tips for creating modern, cloud-native applications. In this article, we'll discuss the benefits of using the 12-Factor principles and demonstrate how they can enhance your apps' performance, maintainability, and adaptability. Let's get started!
What is a 12-factor app?
A 12-Factor app is a method for developing scalable, maintainable, and cloud-native applications by following twelve best practices. It was created by Heroku co-founder Adam Wiggins in 2011 as a methodology for building applications that can easily scale and be deployed in a cloud-based environment. These practices include managing your codebase, handling dependencies, configuring settings, working with backing services, managing processes, and more.
Here are some examples that had accepted this 12-factor app principle: Heroku, Netflix, and Shopify are well-known companies that have implemented the 12-factor app methodology in their applications.
1) Codebase 🌟:

The codebase in a 12-Factor app focuses on maintaining a single code repository for each app. This approach simplifies version control, collaboration, and deployment across various environments.
Example: Using a platform like GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket to manage your codebase allows for easy collaboration and tracking of changes.
2) Dependencies🌈:
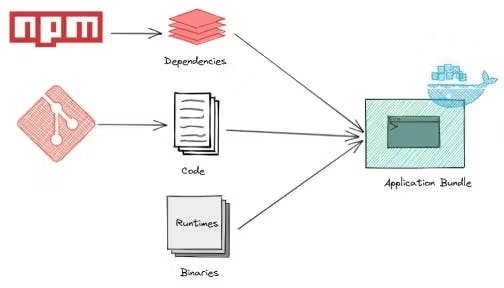
In a 12-factor app, dependencies are explicitly listed, ensuring your app is self-contained. This approach allows for reliable deployment across different environments without unexpected issues.
Example: Utilizing package managers like npm for Node.js or pip for Python helps manage dependencies efficiently.
3) Configuration🌟:
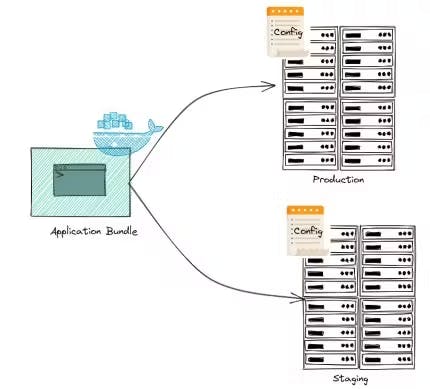
A 12-factor app separates configuration data, such as credentials and environment-specific settings, from the codebase. This separation allows your app to adapt to different environments without code changes, improving security and deployment simplicity.
Example: Using environment variables to store configuration data is a common practice that promotes flexibility.
4) Backing Services🌟:
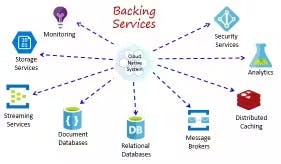
In a 12-factor app, backing services are treated as attached resources, allowing your app to switch and connect to different services without code changes. This approach enhances flexibility and adaptability.
Example: Utilizing environment variables to store database connection strings makes it easy to switch between databases.
5) Build, Release, and Run🌟:
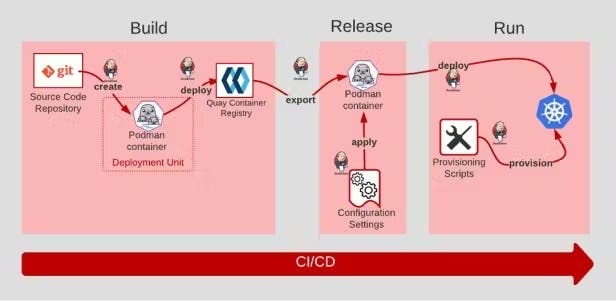
The Build, Release, and Run stages in a 12-factor app involve assembling code and dependencies, creating a release by combining the build with configuration settings and executing the app in the environment. This process streamlines deployment and application management.
Example: Employing continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, such as Jenkins or GitLab CI, can automate these stages.
6) Processes🌟:
12-factor apps focus on stateless, share-nothing processes, allowing your app to scale effortlessly, restart quickly, and remain resilient. This approach simplifies resource allocation and application management.
Example: Implementing stateless RESTful APIs ensures that your app can scale horizontally with ease.
7) Port Binding🌐:
Port binding in a 12-factor app involves having your app listen to a specific port for incoming requests, making it self-sufficient and independent of specific web servers or runtime environments.
Example: Running a Node.js app with Express allows it to bind to a specific port, enabling flexibility in deployment.
8) Concurrency🎉:
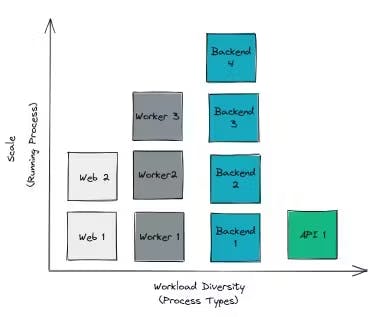
Concurrency in a 12-factor app involves running multiple instances of your app simultaneously to handle increased demand or workload. A Stateless, share-nothing design enables easy horizontal scaling.
Example: Using container orchestration tools like Kubernetes or Docker Swarm helps manage concurrent instances of your app.
9) Disposability :
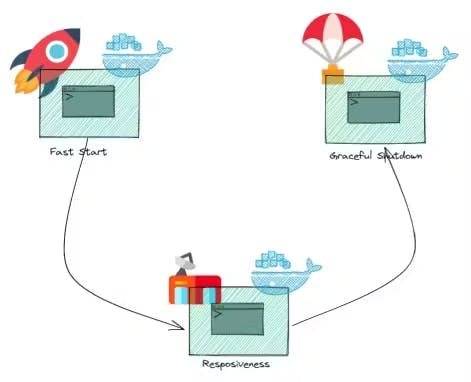
Disposability in a 12-factor app means it can startup, shut down gracefully, and have its instances replaced with ease. This enhances resilience, and resource management, and allows for quick scaling and deployment.
Example: Using Docker containers can improve disposability, as they can be started and stopped quickly and easily replaced.
10) Dev/Prod Parity:
A 12-factor app ensures that development and production environments are similar, reducing inconsistencies and streamlining the development process.
Example: Using the same tools, services, and configurations across environments helps identify issues early and simplifies deployment.
11) Logs😊:
In a 12-factor app, logs are treated as event streams, allowing your app to focus on outputting logs without worrying about storage or management.
Example: Using log aggregation tools like Logstash or Fluentd can centralize, analyze, and monitor logs.
12) Admin Processes🌟:
Admin processes in a 12-factor app are one-time tasks or management jobs that run separately from regular app processes, using the same codebase, environment, and settings to maintain consistency and ease of maintenance.
Example: Running database migrations or data cleanup tasks as separate processes ensures that they do not interfere with the running app.
Resources :
The 12-Factor App official website: https://12factor.net/
The Twelve-Factor App on GitHub: https://github.com/heroku/12factor
The 12-Factor App: A Java Developer's Perspective: https://dzone.com/articles/the-12-factor-app-a-java-developers-perspective
The 12-Factor App Methodology Explained: https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/the-12-factor-app-methodology-explained
Building 12-Factor Microservices on AWS: https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/compute/building-12-factor-microservices-on-aws/
12 Factor App By KodeCloud :
Conclusion :
In conclusion, adhering to the 12-Factor methodology can significantly enhance your app's performance, maintainability, and adaptability. By following these best practices, you can build scalable, cloud-native applications that can easily adapt to changing business requirements and technological advancements.
And it's a wrap-up 🙂. I hope you have learned something from this blog. If it's helpful to you then do like ❤, follow🤝 me on Hashnode, Twitter, and GitHub subscribe to my Hashnode newsletter so that you don't miss any future posts. Thanks for reading and have a great day!